1: History and Motivation
Examine the evolution of virtualization technologies from bare metal, virtual machines, and containers and the tradeoffs between them.
2: Technology Overview
Explores the three core Linux features that enable containers to function (cgroups, namespaces, and union filesystems), as well as the architecture of the Docker components.
3: Installation and Set Up
Install and configure Docker Desktop
4: Using 3rd Party Container Images
Use publicly available container images in your developer workflows and learn how about container data persistence.
5: Example Web Application
Building out a realistic microservice application to containerize.
6: Building Container Images
Write and optimize Dockerfiles and build container images for the components of the example web app.
7: Container Registries
Use container registries such as Dockerhub to share and distribute container images.
8: Running Containers
Use Docker and Docker Compose to run the containerized application from Module 5.
9: Container Security
Learn best practices for container image and container runtime security.
10: Interacting with Docker Objects
Explore how to use Docker to interact with containers, container images, volumes, and networks.
11: Development Workflow
Add tooling and configuration to enable improved developer experience when working with containers.
•Developer Experience Wishlist
12: Deploying Containers
Deploy containerized applications to production using a variety of approaches.

Docker System Components:
It is useful to break down the various components within the Docker ecosystem.
Docker Desktop is an application you install on development systems that provides:
- A client application:
- Command Line Interface (CLI): Interact with Docker using commands like
docker runordocker pull. - Graphical User Interface (GUI): Browse images, configure CPU, memory, and disk space allocation.
- Credential Helper: Store credentials for private registries.
- Extensions: Third-party software that provides additional functionality.
- Command Line Interface (CLI): Interact with Docker using commands like
- A Linux virtual machine containing:
- Docker daemon (dockerd): Manages container objects, networking, and volumes within the server host application. It exposes the Docker API for communication with the client application.
- (Optional) Kubernetes cluster
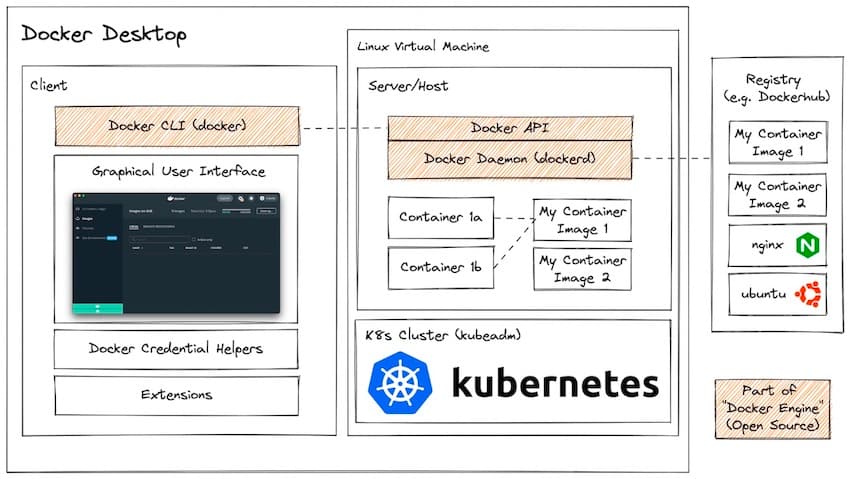
Docker Engine vs Docker Desktop
There is often confusion between "Docker Desktop" and "Docker Engine". Docker Engine refers specifically to a subset of the Docker Desktop components which are free and open source and can be installed only on Linux.
Docker Engine includes:
- Docker Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Docker daemon (dockerd), exposing the Docker Application Programming Interface (API)
Docker Engine can build container images, run containers from them, and generally do most things that Docker Desktop but is Linux only and doesn't provide all of the developer experience polish that Docker Desktop provides.
For more information about docker engine see: https://docs.docker.com/engine/
Container Registries
Container image registries are not part of Docker itself, but because they are the primary mechanism for storing and sharing container images it is worth including it here. Docker runs a registry named DockerHub, but there are many other registries as well. More info on these can be found in Module 7: Container Registries.