1: History and Motivation
Examine the evolution of virtualization technologies from bare metal, virtual machines, and containers and the tradeoffs between them.
2: Technology Overview
Explores the three core Linux features that enable containers to function (cgroups, namespaces, and union filesystems), as well as the architecture of the Docker components.
3: Installation and Set Up
Install and configure Docker Desktop
4: Using 3rd Party Container Images
Use publicly available container images in your developer workflows and learn how about container data persistence.
5: Example Web Application
Building out a realistic microservice application to containerize.
6: Building Container Images
Write and optimize Dockerfiles and build container images for the components of the example web app.
7: Container Registries
Use container registries such as Dockerhub to share and distribute container images.
8: Running Containers
Use Docker and Docker Compose to run the containerized application from Module 5.
9: Container Security
Learn best practices for container image and container runtime security.
10: Interacting with Docker Objects
Explore how to use Docker to interact with containers, container images, volumes, and networks.
11: Development Workflow
Add tooling and configuration to enable improved developer experience when working with containers.
•Developer Experience Wishlist
12: Deploying Containers
Deploy containerized applications to production using a variety of approaches.

Understanding the Docker Build Process
What is a Dockerfile?
A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands required to create and assemble a container image. It serves as a recipe for your application, starting with a base layer like an operating system, installing language runtime and dependencies, setting up the execution environment, and finally running a command to start your application.
👨🍳 Application Recipe:
---------------------------------------
1. Start with an Operating System
2. Install the language runtime
3. Install any application dependencies
4. Set up the execution environment
5. Run the application
The Docker Build Context
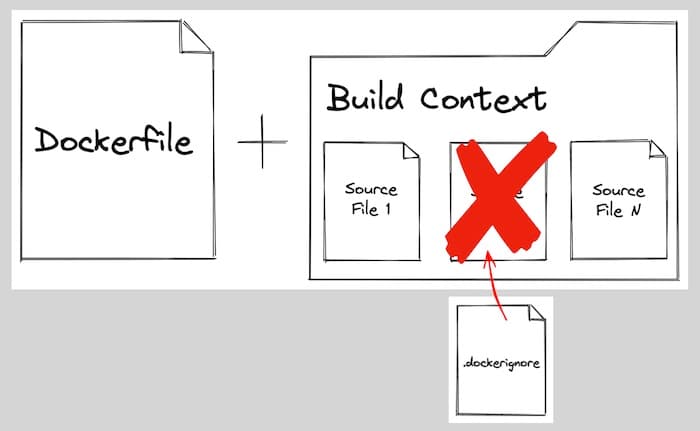
The Dockerfile is paired with a build context, which is usually a folder or directory on your local system containing your source code. The build context can also be a URL, such as a public GitHub repository. Docker uses the Dockerfile and build context together when running the docker build command to produce a container image.
The .dockerignore File
A .dockerignore file can be included in your build context to tell Docker to ignore certain files. For example, if you've installed node_modules locally, you wouldn't want to copy those into the container image, as they will be installed within the Dockerfile. This can prevent incompatibilities between installations on your host system and within the container.
Writing a Dockerfile
When writing a Dockerfile, you can refer to the Docker documentation for a list of valid commands. The format for a Dockerfile is relatively simple:
A hash (#) is used for comments. Instructions are written in all caps, followed by arguments. For example:
# This step installs dependencies
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y <package_name>
Common Commands in a Dockerfile
Here are some you'll encounter in almost every Dockerfile:
FROM: Specifies the base layer or operating system for the container image.
RUN: Executes a command during the build phase.
COPY: Copies files from the build context (e.g., your local system) to the container image.
CMD: Provides a command to be executed when the container starts.
Docker build command
We can take a Dockerfile and a build context and use the docker build command to create a Docker Container Image!
docker build -f Dockerfile .
Here the . indicates that the current directory should be used as the build context.
Note: You only have to pass a Dockerfile name if it is named something other than "Dockerfile"